-
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
Create Object
Series Data 형성
obj = pd.Series([1,3,5,np.nan,6,8]) obj => 0 1.0 1 3.0 2 5.0 3 NaN 4 6.0 5 8.0 dtype: float64DataFrame Data 형성
import pandas as pd import numpy as np dates = pd.date_range('20200902', periods=6) dates=> DatetimeIndex(['2020-09-02', '2020-09-03', '2020-09-04', '2020-09-05', '2020-09-06', '2020-09-07'], dtype='datetime64[ns]', freq='D') df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randn(6,4), index=dates, columns=list('ABCD')) df=> A B C D 2020-09-02 0.676201 -0.735438 0.312747 -1.843620 2020-09-03 -0.358015 1.128569 0.738395 0.170064 2020-09-04 -1.307082 -0.417756 0.165525 -1.152548 2020-09-05 0.210957 -1.450819 -1.006740 1.197188 2020-09-06 0.554652 -1.910535 -1.145034 -0.563270 2020-09-07 -0.417373 2.479437 -1.287300 -1.128281 df2 = pd.DataFrame({'A':1., 'B':pd.Timestamp('20200902'), 'C':pd.Series(1,index=list(range(4)),dtype='float32'), 'D':np.array([3]*4, dtype='int32'), 'E':pd.Categorical(["test","train","test","train"]), 'F':'Foo' }) df2=> A B C D E F 0 1.0 2020-09-02 1.0 3 test Foo 1 1.0 2020-09-02 1.0 3 train Foo 2 1.0 2020-09-02 1.0 3 test Foo 3 1.0 2020-09-02 1.0 3 train Foo df2.dtypes A float64 B datetime64[ns] C float32 D int32 E category F object dtype: object #최상단 데이터 보여주기 df2.head() A B C D E F 0 1.0 2020-09-02 1.0 3 test Foo 1 1.0 2020-09-02 1.0 3 train Foo 2 1.0 2020-09-02 1.0 3 test Foo #최하단 데이터 보여주기 df2.tail() A B C D E F 1 1.0 2020-09-02 1.0 3 train Foo 2 1.0 2020-09-02 1.0 3 test Foo 3 1.0 2020-09-02 1.0 3 train Foo #인덱스 보여주기 df2.index Int64Index([0, 1, 2, 3], dtype='int64') #컬럼 보여주기 df2.columns Index(['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F'], dtype='object') #DataFrame을 Array로 바꾸기 df2.to_numpy() [[1.0 Timestamp('2020-09-02 00:00:00') 1.0 3 'test' 'Foo'] [1.0 Timestamp('2020-09-02 00:00:00') 1.0 3 'train' 'Foo'] [1.0 Timestamp('2020-09-02 00:00:00') 1.0 3 'test' 'Foo'] [1.0 Timestamp('2020-09-02 00:00:00') 1.0 3 'train' 'Foo']] #DataFrame Data를 간단하게 분석하기 df2.describe() A C D count 4.0 4.0 4.0 mean 1.0 1.0 3.0 std 0.0 0.0 0.0 min 1.0 1.0 3.0 25% 1.0 1.0 3.0 50% 1.0 1.0 3.0 75% 1.0 1.0 3.0 max 1.0 1.0 3.0 #축 변경 df2.T 0 ... 9 A 1 ... 1 B 2020-09-02 00:00:00 ... 2020-09-02 00:00:00 C 1 ... 1 D 3 ... 3 E test ... train F Foo ... Foo # Sort by Axis df2.sort_index(axis=(중심선 위치), ascending=False(내림차순)) F E D C B A 0 Foo test 3 1.0 2020-09-02 1.0 1 Foo train 3 1.0 2020-09-02 1.0 2 Foo test 3 1.0 2020-09-02 1.0 3 Foo train 3 1.0 2020-09-02 1.0 4 Foo test 3 1.0 2020-09-02 1.0 5 Foo train 3 1.0 2020-09-02 1.0 6 Foo test 3 1.0 2020-09-02 1.0 7 Foo train 3 1.0 2020-09-02 1.0 8 Foo test 3 1.0 2020-09-02 1.0 9 Foo train 3 1.0 2020-09-02 1.0 # Sort by Values df2.sort_values(by ='B') A B C D E F 0 1.0 2020-09-02 1.0 3 test Foo 1 1.0 2020-09-02 1.0 3 train Foo 2 1.0 2020-09-02 1.0 3 test Foo 3 1.0 2020-09-02 1.0 3 train Foo 4 1.0 2020-09-02 1.0 3 test Foo 5 1.0 2020-09-02 1.0 3 train Foo 6 1.0 2020-09-02 1.0 3 test Foo 7 1.0 2020-09-02 1.0 3 train Foo 8 1.0 2020-09-02 1.0 3 test Foo 9 1.0 2020-09-02 1.0 3 train Foo # column 의 값 가져오기 df2['E'] 0 test 1 train 2 test 3 train 4 test 5 train 6 test 7 train 8 test 9 train Name: E, dtype: category Categories (2, object): [test, train] #index 기준으로 df2[0:3] A B C D E F 0 1.0 2020-09-02 1.0 3 test Foo 1 1.0 2020-09-02 1.0 3 train Foo 2 1.0 2020-09-02 1.0 3 test Foo #label 기준으로 선택 df.loc[dates[0]] A -0.803974 B 0.352322 C 1.124562 D 1.152973 #multi-axis label pick df.loc[:,['A','B']] A B 2020-09-02 -0.535334 -0.440890 2020-09-03 0.799865 -1.641966 2020-09-04 -0.875538 0.378988 2020-09-05 -1.348886 -1.900768 2020-09-06 2.371218 1.130410 2020-09-07 0.482218 -0.409745 #position 기준 1번 row의 data 값 df2.iloc[1] A 1 B 2020-09-02 00:00:00 C 1 D 3 E train F Foo Name: 3, dtype: object #slicing df2.iloc[1:2,3:5] D E 1 3 train #Boolean을 통해 즉 조건문을 통한 조회 가능 #column 추가 df2['G'] = ['one', 'one', 'two', 'three', 'four', 'three', 'two', 'three', 'four', 'three'] df2 => A B C D E F G 0 1.0 2020-09-02 1.0 3 test Foo one 1 1.0 2020-09-02 1.0 3 train Foo one 2 1.0 2020-09-02 1.0 3 test Foo two 3 1.0 2020-09-02 1.0 3 train Foo three 4 1.0 2020-09-02 1.0 3 test Foo four 5 1.0 2020-09-02 1.0 3 train Foo three 6 1.0 2020-09-02 1.0 3 test Foo two 7 1.0 2020-09-02 1.0 3 train Foo three 8 1.0 2020-09-02 1.0 3 test Foo four 9 1.0 2020-09-02 1.0 3 train Foo three #isin을 사용하여 값을 가지고 있는지 확인 df2[df2['G'].isin(['two','four'])] A B C D E F G 2 1.0 2020-09-02 1.0 3 test Foo two 4 1.0 2020-09-02 1.0 3 test Foo four 6 1.0 2020-09-02 1.0 3 test Foo two 8 1.0 2020-09-02 1.0 3 test Foo four #Setting 새로운 컬럼에 값 자동으로 할당. s1 = pd.Series([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6], index=pd.date_range('20200902', periods=6)) s1 => 2020-09-02 1 2020-09-03 2 2020-09-04 3 2020-09-05 4 2020-09-06 5 2020-09-07 6 Freq: D, dtype: int64Axis?
다차원 배열의 축(axis)
다차원 배열의 경우 그림과 같은 축을 갖습니다.
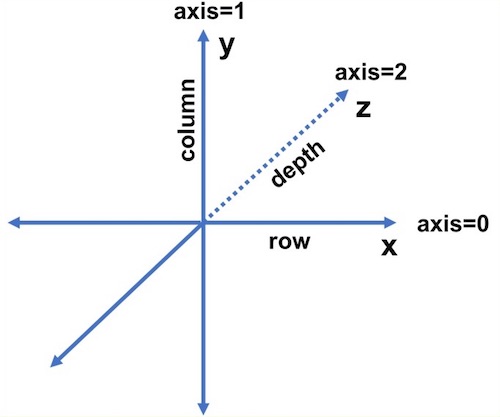
벡터는 x 축만을 갖는 자료형입니다. 1차원 배열에 해당하는 벡터의 각 요소(Element)는 그 자체가 Row입니다.
2차원 배열 형태의 행렬(matrix)은 x축의 행과 y축의 컬럼을 갖습니다. 2차원 배열 행렬은 depth가 1이라고 생각할 수 있습니다.
3차원 배열 형태의 Tensor는 행과 열을 갖고 각 컬럼은 벡터 형태를 갖습니다. 이러한 벡터를 Depth로 표현합니다.
4차원 이상의 배열은 z축의 depth 요소가 스칼라가 아니라 벡터 이상의 자료형을 갖는 것을 의미합니다. 이러한 방식으로 데이터의 Dimension(차원)은 끝없이 확장될 수 있습니다.
axis = 0 기준 row 기준 합
axis = 1 기준 column 기준 합
누락된 데이터는 NaN으로 표시
누락된 데이터를 버리는 방법
df2.dropna(how='any')
누락된 데이터를 채우는 방법
df2.fillna(value=5)
누락된 데이터인지 확인하는 방법
pandas.isna(df2)
통계 값
df2.mean()
다른 축에서 동일한 작업
df2.mean(1)
문자열 병합
concat
그룹화
groupby('A') column을 기준으로 group화
'개발' 카테고리의 다른 글
AWS EC2 환경에 nginx를 설치해 배포하는 방법. (0) 2020.10.21 [Linux] Ununtu에서 MariaDB 설치 하기 (0) 2020.10.21 https 적용하기 (0) 2020.08.12 mysql errno :150 ?~? (0) 2020.08.02 Vue 에서 is not Defined 가 뜬다면? (0) 2020.07.25